
Healthy neonates of 36 weeks gestation and older: It should only be used when the serious risk involved is considered justified.Prophylaxis of vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB) Therefore, the intravenous route should be avoided unless it is strictly necessary.

Some animals have exhibited these severe reactions, especially on receiving the drug for the first time. These severe reactions have resembled hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis, including shock and cardiac and/or respiratory arrest. Severe reactions, including fatalities, may occur during and immediately after intravenous injection, if precautions have not been taken to dilute the drug and if above infusion rate guidelines are not followed. In case of liver diseases, large doses of Vitamin K1 do not guarantee the success of the treatment, if response to initial therapy is unsatisfactory.įailure to respond to Vitamin K1 indicates that the dosage schedule should be adjusted. Phytonadione (Vitamin K1) will not counteract the effect of heparin. Whole blood or blood serum therapy may be necessary if the bleeding is severe. A minimum of 1 to 2 hours is required for measurable improvements in the prothrombin time. Immediate coagulant effect should not be expected after administration of the drug. When dilutions are indicated, administration should be started immediately after mixing with the diluent, and unused portions of the solution should be discarded. In some cases, when the drug needs to be administered by the IV route, it may be necessary to dilute it with 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution, Dextrose solution (5%), or with a mixture of Dextrose solution (5%) and 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution in equal parts in order to facilitate slow administration. The smallest effective dose should be sought to minimize the risk of adverse reaction. In the event of shock or excessive blood loss, the use of whole blood or component therapy is indicated.
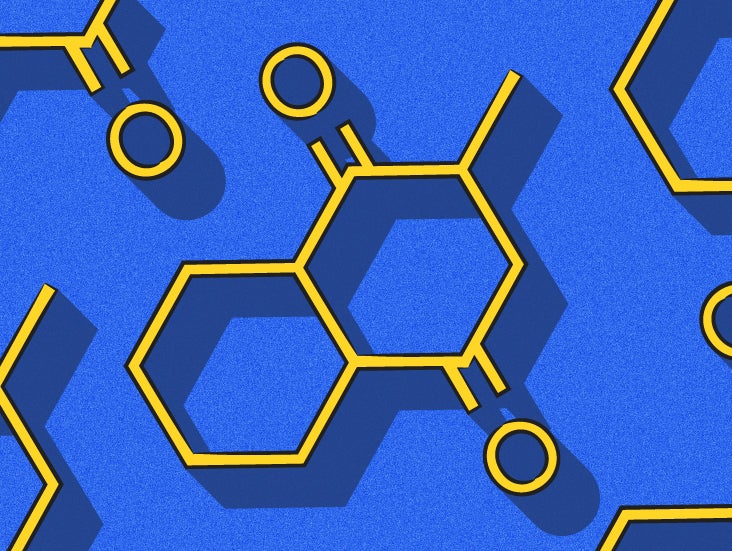
If 6 or 8 hours after parenteral administration of Vitamin K1 the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should be repeated.

Monitor prothrombin time and adjust dose accordingly.įrequency and amount of doses should be determined by prothrombin time response and clinical condition. If IV administration is essential, the drug shall be administered slowly, at the indicated rate. Whenever possible, the drug shall be administered IM or SC. Hypersensitivity to any of the components in the formulation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
